Periodic Table Of Heavy Metals
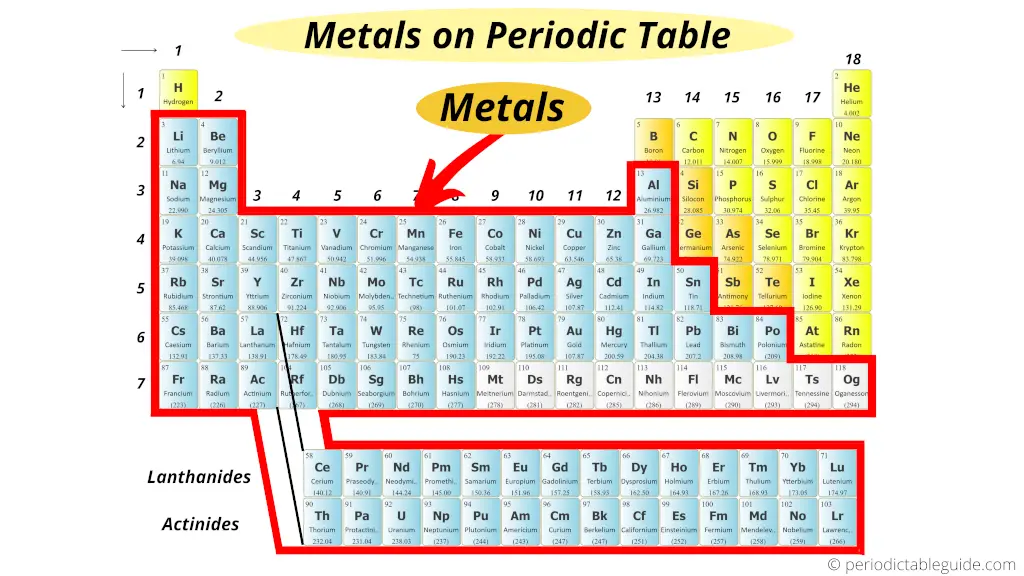
The metals are located on the left side of the Periodic Tabular array.
This is the short and uncomplicated respond of your question "Where are Metals located on the Periodic Table?"
Merely expect…
At that place are lot more things you demand to know near the metals of the Periodic table, like;
- Alkali metals on Periodic table
- Alkaline Earth metals on Periodic tabular array
- Transition metals on Periodic table
- Inner transition metals on Periodic table
- How many metals are in that location on Periodic table?
- Rare Globe metals on Periodic table
- Heavy metals on Periodic table
- Reactive metals on Periodic table
- The complete list of all metals
- Why are metals on the left of Periodic table?
- Properties of metals
- Physical properties of metals
- Chemical properties of metals
- And lots more…
Let's dive directly into it.
What are metals in Periodic table?
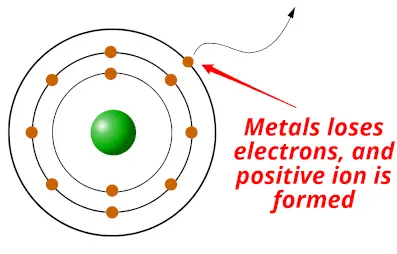
Metals are the elements which take the tendency to donate or lose electrons to form positive ions.
In brusque remember that;
- Metals are electron donors (metals loses / donates electrons)
The elements which prove this type of nature (nature of losing electrons) are known as metals.
Now in the Periodic table, these metals are plant on the left side.
Simply these metals are farther classified into many more than types.
Allow me tell you few things about the types of metals on the Periodic table.
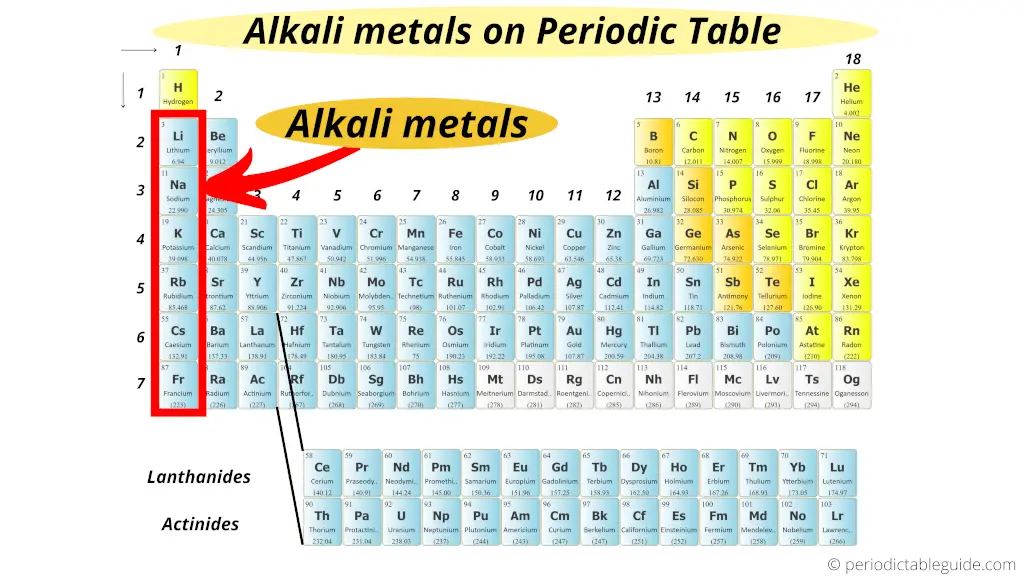
The left most elements on the Periodic table (group 1 elements) are known as alkali metals.
But do yous know;
What are alkali metals? And why the brine metals are called so?
The elementary answer: Alkali metals grade an alkaline metal solution (basic solution) when they react with h2o.
That'south why they are known as alkali metals. (Read detailed explanation from hither.)
Also visit: Why are alkali metals so reactive?
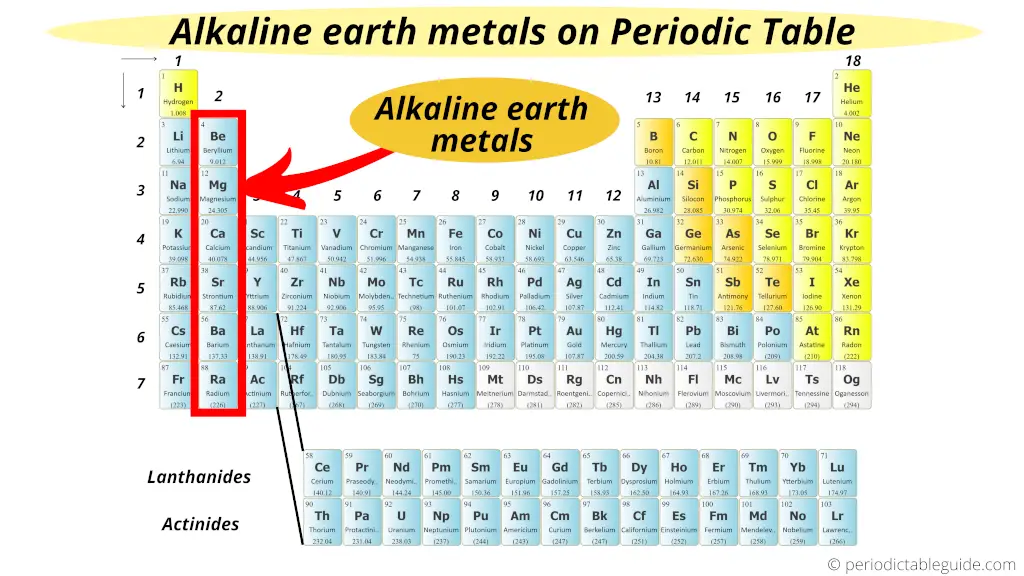
The Alkaline Earth metals are located in the 2nd group of Periodic tabular array.
Now once again I will tell you a simple reason why these group 2 elements are known every bit Alkaline Earth Metals.
See, the group two elements take almost similar properties that of the group one elements (Brine Metals).
Just the difference is that they are mostly establish from the earth crust.
Thus they are known equally Alkaline Earth Metals.
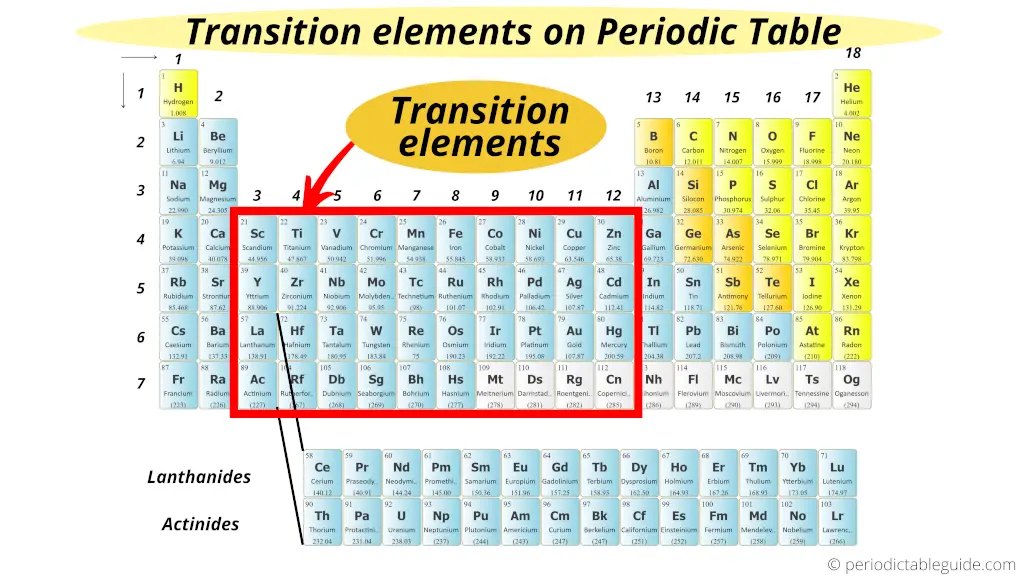
The elements lying in group 3 to group 12 are known equally Transition metals (or transition elements).
Transition metals form a span between the chemically active metals of s-block elements and the less active elements of Groups thirteen and 14.
Thus these metals are known as "Transition metals".
Also visit: How many transition metals are there on periodic table?
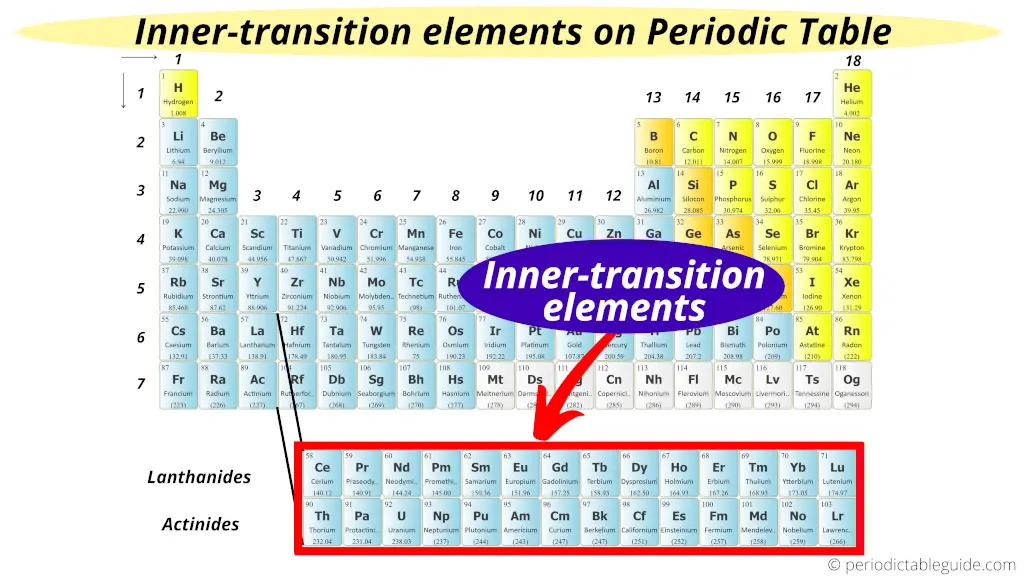
The two bottom rows in the Periodic tabular array are called inner transition metals.
Why?
But equally the proper name suggests, they are transition metals only, but they are lying in the inner section of the transition metals.
Hence they are named as inner transition metals (or inner transition elements)
The elements of the first row are known as Lanthanides and the elements of the 2nd row are known as Actinides.
Also visit:
1). Why are inner transition metals at the lesser of periodic table?
2). Difference between transition and inner transition elements.
Short answer: I don't know exactly (lol…)
Allow me explain to you why I do not know this answer.
A general question which all students have is about the total number of metals on the Periodic table.
Well, there is not the verbal reply to this question.
But out of the full 118 known elements, more than 78% of the elements testify metallic character.
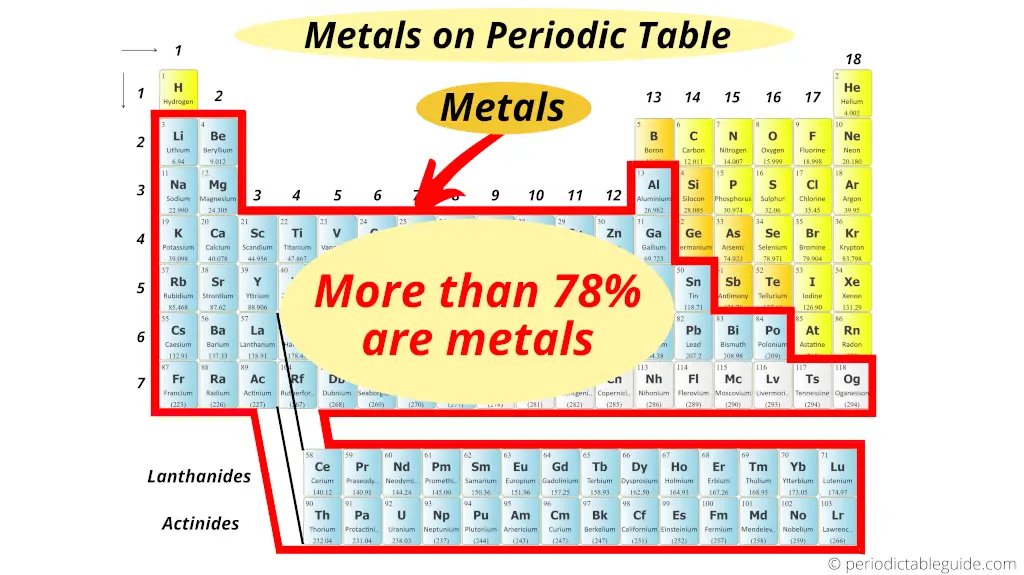
Out of the 118 elements of periodic tabular array, approximately 94 elements are metals (but this is not the exact number).
Reason?
According to wikipedia, this number is inexact because the boundaries between metals, nonmetals and metalloids fluctuate slightly due to lack of universally accustomed definitions.
(That means in metallurgy, the researchers may define metals on the basis of density. In physics, they may define metals on the basis of physical properties. And in chemistry, the chemists are concerned with the chemical properties of metals.)
Also the elements which are shown in grey color are still under research work by the researchers (elements 109 to 118 mentioned in grey color).
These are the synthetic elements and they have a very short one-half life.
This is the reason why the total number of metals are still not known.
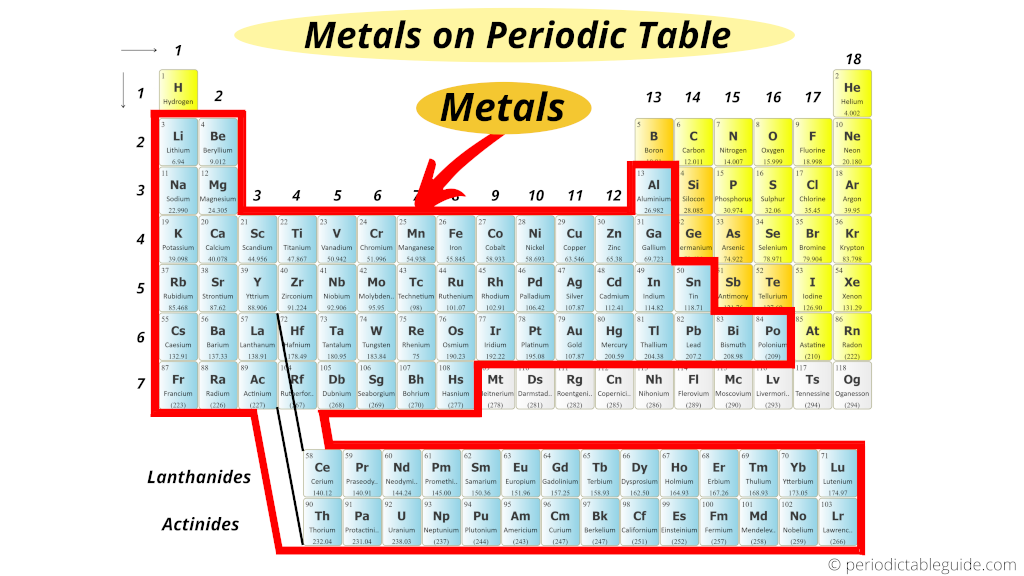
So to be exact, if we consider the beginning 108 elements, and then there are total 84 metals present on Periodic table.
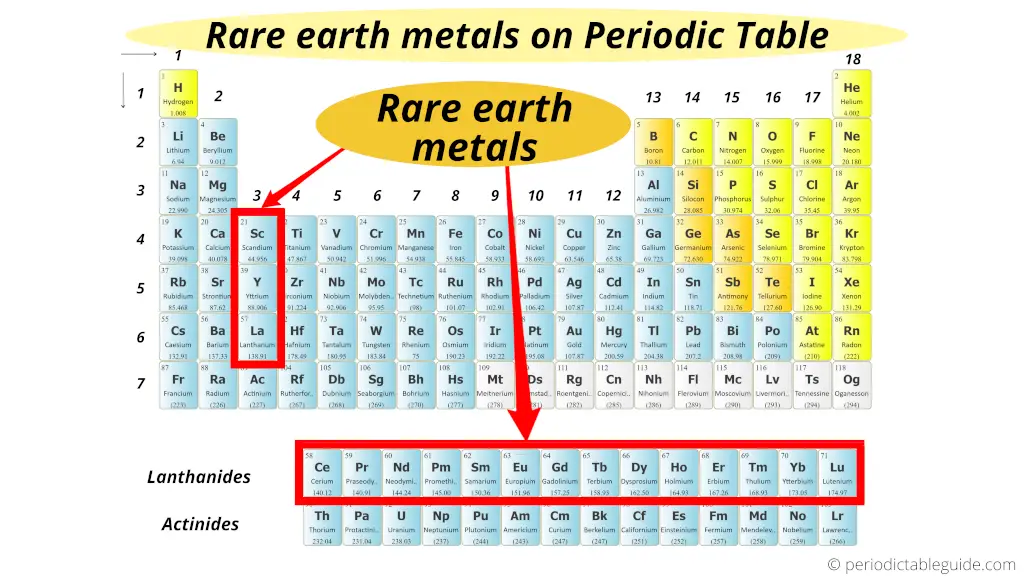
There are total 17 Rare Globe metals on the Periodic table. Rare World Metals includes all the fifteen Lanthanides as well as scandium(Sc) and yttrium (Y). Then full fifteen + two = 17 Rare Globe metals.
Here is a consummate list of all the 17 rare globe metals.
| Diminutive number | Symbol | Name of element |
| 21 | Sc | Scandium |
| 39 | Y | Yttrium |
| 57 | La | Lanthanum |
| 58 | Ce | Cerium |
| 59 | Pr | Praseodymium |
| 60 | Nd | Neodymium |
| 61 | Pm | Promethium |
| 62 | Sm | Samarium |
| 63 | Eu | Europium |
| 64 | Gd | Gadolinium |
| 65 | Tb | Terbium |
| 66 | Dy | Dysprosium |
| 67 | Ho | Holmium |
| 68 | Er | Erbium |
| 69 | Tm | Thulium |
| lxx | Yb | Ytterbium |
| 71 | Lu | Lutetium |
Merely do you know why they are chosen rare?
Why Rare World metals are called so?
Answer: You might be thinking that rare means these elements are available in very less quantity.
Only if you are thinking so, so you lot are incorrect.
Rare earth metals are not actually that rare as the name suggests.
Fifty-fifty, they are available in more than abundant quantities than aureate.
But the fact is that they are spread evenly on the earth and information technology is very difficult to observe these elements at one place on the earth.
Thus they are rare in the context of available resources.
First of all,
What are heavy metals?
The heavy metals are those metals which possess higher density or higher diminutive mass.
Well, the definition of heavy metals may differ in metallurgy, physics also as chemistry.
In metallurgy, researchers define heavy metals on the basis of density.
While in physics, they may use diminutive numbers for defining heavy metals.
Whereas in chemistry, chemists are concerned with the chemical properties of heavy metals for defining them.
Then in that location is a research piece of work still going on for the specific definition and nomenclature of heavy metals.
Many researchers use the mutual criteria that if the metals have the density of more than than 5 g/cm³, then they are probable to be known equally heavy metals.
On the basis of this criteria, the heavy metals are shown on the Periodic table.
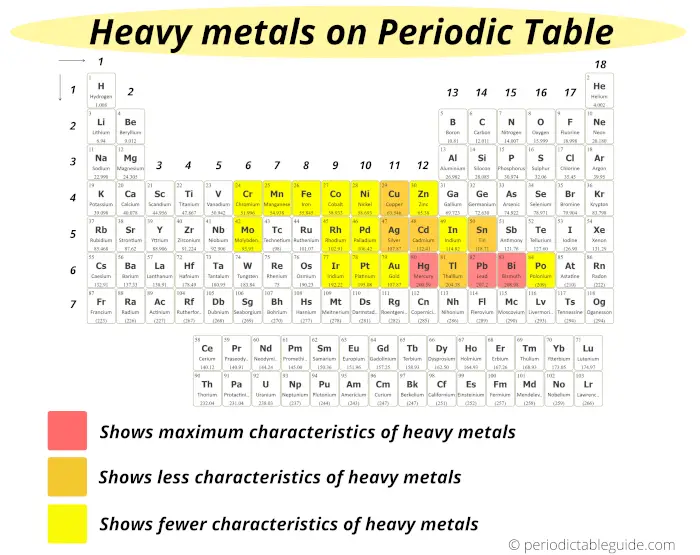
The metals which show maximum characteristics of heavy metals are;
- Mercury (Hg)
- Lead (Pb) and
- Bismuth (Bi)
These heavy metals are displayed on the Periodic table with red colour (meet above image)
The metals which evidence less characteristics of heavy metals are;
- Copper (Cu)
- Silver (Ag)
- Cadmium (Cd)
- Tin (Sn)
- Thallium (Tl)
And these elements are represented by orange color on the Periodic tabular array.
Residual of the elements which are shown in yellow color show fewer characteristics of heavy metals.
Here I'll tell you about the most reactive metallic on the Periodic table. Only before that, allow us discuss what is a reactivity in metals?
What are reactive metals?
Reactive metals are those metals which show high tendency to lose electron/south in a chemical reaction.
For case, as we motility down the group, the atomic size increases.
Thus the force of attraction between nucleus and outermost electrons decreases.
Because of this, the electron will exist lost easily during chemic reaction.
Hence, down the grouping, as the atomic size increases, the reactivity of metals increases.
Well-nigh reactive metallic on Periodic table
The highly reactive metals are located on the left lesser corner of the Periodic table. They are the Alkali metals of group 1.
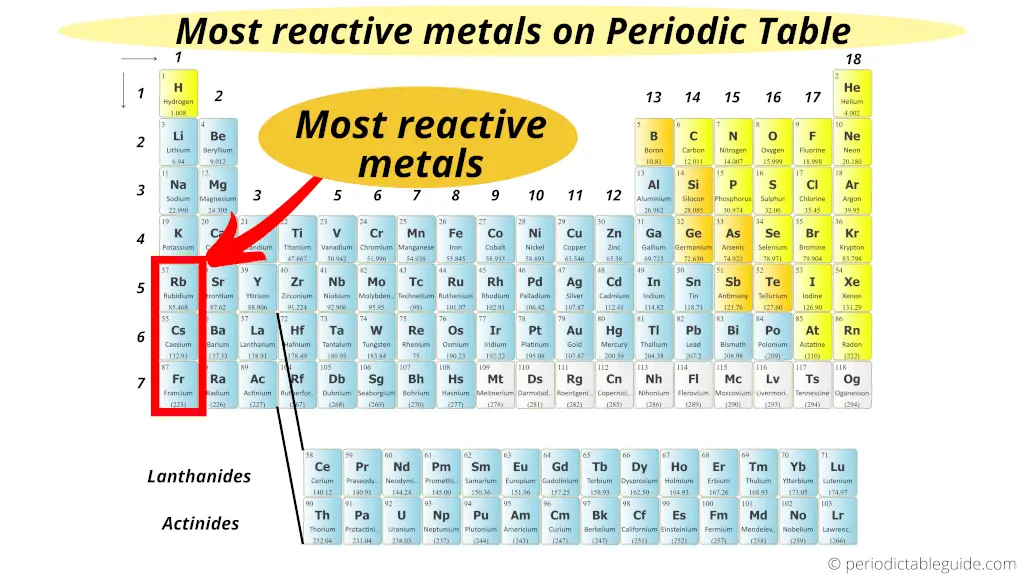
In 1st grouping, every bit we motion down from tiptop to lesser, the reactive of metals increases.
Thus the lesser nearly element of group 1 (i.e francium) is the most reactive metal on the Periodic tabular array.
(Note: Francium is a laboratory made chemical element. It is available in a very less quantity. And hence for whatsoever applied purposes, caesium is considered as the virtually reactive metal in Periodic table. Caesium has high reactivity, simply it is predicted that Francium would have fifty-fifty higher reactivity than that of caesium)
Besides see: Reactivity of alkali metals with water (Explained with animation)
| Atomic number | Symbol | Name of element |
| 3 | Li | Lithium |
| iv | Exist | Beryllium |
| 11 | Na | Sodium |
| 12 | Mg | Magnesium |
| xiii | Al | Aluminum |
| 19 | Grand | Potassium |
| 20 | Ca | Calcium |
| 21 | Sc | Scandium |
| 22 | Ti | Titanium |
| 23 | V | Vanadium |
| 24 | Cr | Chromium |
| 25 | Mn | Manganese |
| 26 | Fe | Iron |
| 27 | Co | Cobalt |
| 28 | Ni | Nickel |
| 29 | Cu | Copper |
| 30 | Zn | Zinc |
| 31 | Ga | Gallium |
| 37 | Rb | Rubidium |
| 38 | Sr | Strontium |
| 39 | Y | Yttrium |
| 40 | Zr | Zirconium |
| 41 | Nb | Niobium |
| 42 | Mo | Molybdenum |
| 43 | Tc | Technetium |
| 44 | Ru | Ruthenium |
| 45 | Rh | Rhodium |
| 46 | Pd | Palladium |
| 47 | Ag | Silvery |
| 48 | Cd | Cadmium |
| 49 | In | Indium |
| fifty | Sn | Tin can |
| 55 | Cs | Caesium |
| 56 | Ba | Barium |
| 57 | La | Lanthanum |
| 58 | Ce | Cerium |
| 59 | Pr | Praseodymium |
| sixty | Nd | Neodymium |
| 61 | Pm | Promethium |
| 62 | Sm | Samarium |
| 63 | Eu | Europium |
| 64 | Gd | Gadolinium |
| 65 | Tb | Terbium |
| 66 | Dy | Dysprosium |
| 67 | Ho | Holmium |
| 68 | Er | Erbium |
| 69 | Tm | Thulium |
| lxx | Yb | Ytterbium |
| 71 | Lu | Lutetium |
| 72 | Hf | Hafnium |
| 73 | Ta | Tantalum |
| 74 | Due west | Tungsten |
| 75 | Re | Rhenium |
| 76 | Bone | Osmium |
| 77 | Ir | Iridium |
| 78 | Pt | Platinum |
| 79 | Au | Gold |
| 80 | Hg | Mercury |
| 81 | Tl | Thallium |
| 82 | Atomic number 82 | Lead |
| 83 | Bi | Bismuth |
| 84 | Po | Polonium |
| 87 | Fr | Francium |
| 88 | Ra | Radium |
| 89 | Air-conditioning | Actinium |
| 90 | Th | Thorium |
| 91 | Pa | Protactinium |
| 92 | U | Uranium |
| 93 | Np | Neptunium |
| 94 | Pu | Plutonium |
| 95 | Am | Americium |
| 96 | Cm | Curium |
| 97 | Bk | Berkelium |
| 98 | Cf | Californium |
| 99 | Es | Einsteinium |
| 100 | Fm | Fermium |
| 101 | Md | Mendelevium |
| 102 | No | Nobelium |
| 103 | Lr | Lawrencium |
| 104 | Rf | Rutherfordium |
| 105 | Db | Dubnium |
| 106 | Sg | Seaborgium |
| 107 | Bh | Bohrium |
| 108 | Hs | Hassium |
| 109 | Mt | Meitnerium |
| 110 | Ds | Darmstadtium |
| 111 | Rg | Roentgenium |
| 112 | Cn | Copernicium |
| 113 | Nh | Nihonium |
| 114 | Fl | Flerovium |
| 115 | Mc | Moscovium |
| 116 | Lv | Livermorium |
| 117 | Ts | Tennessine |
| 118 | Og | Oganesson |
Do yous know what is the primary holding of metal?
They lose electron/s during the chemical reaction.

Now only think, what should exist the conditions or properties that an chemical element should possess to make the electron lost hands.
Here are few properties necessary for easy loss of electrons.
- Element should take depression ionization free energy
- Element should accept less number of electrons in outermost orbit
- Element should have less electronegativity
If the elements possess these properties, and then they will comport like metals.
Now, you know that the elements on the left side of Periodic table have less valence electrons in their outermost orbit.
Also the atomic size of these elements are more than, which is favorable for the loss of electrons.
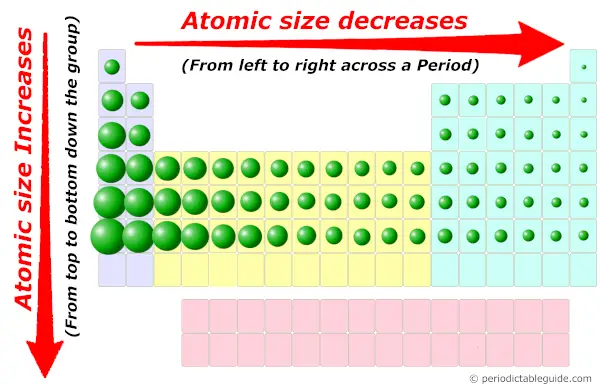
As they possess bigger atomic size, it is like shooting fish in a barrel to remove the valence electrons from the outermost orbit. So they have depression ionization energy.
Too these elements located on the left side have less electronegativity.
Let me give y'all a short introduction about electronegativity.
Electronegativity is a tendency to attract the electron pair.
I have discussed this in detailed article of Periodic table that electronegativity depends upon the size of an atom.
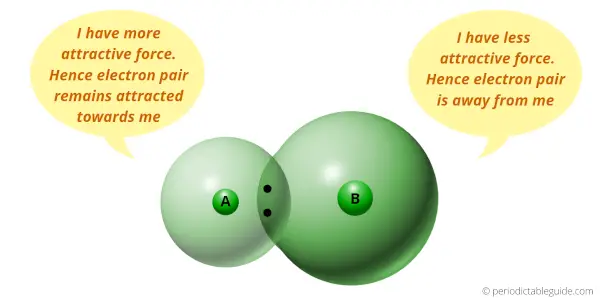
If diminutive size is less, then it has more tendency to concenter the electron pair (ways smaller the size, more is the electronegativity.) And if the atomic size is more, and then it has less trend to attract the electron pair (means bigger the size, lesser is the electronegativity.)
Now the elements on the left side of Periodic table have more than atomic size. Then they volition have less electronegativity.
Hence, they are more metallic in nature.
I hope, now you accept got the answer of "Why metals are located on the left side of Periodic table?"
Here I'll bear witness you lot the physical and chemical properties of metals.
Keep reading…
Physical properties of metal
#1 Sonorous

Metals produce ringing sound when they are stuck hard. This indicates that metals are sonorous in nature.
For case: Ringing of bell.
#2 Solid state at room temperature
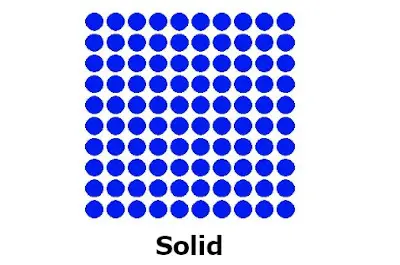
All the metals are solids at room temperature (except mercury)
They have definite shape and size.
#3 Lustrous (shiny)

Metals are Lustrous.
They have a smoothen shiny surface.
#4 Malleability

Metals tin be reshaped into sparse sheets on applying sufficient pressure on it. This property of metals is known every bit malleability.
#v Ductility
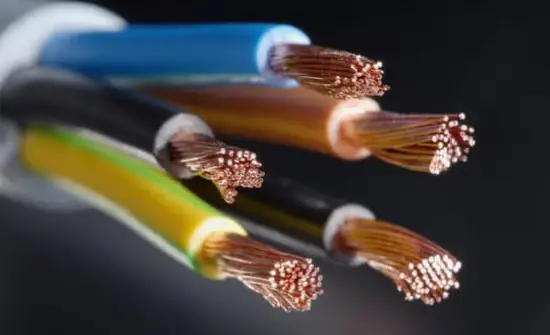
Metals can exist fatigued into thin wires. (For example cable wires, thin copper wires used in electrical circuit used in your laptop or phone which you lot are holding correct now, etc …)
#6 Electrical conductivity

Metals are proficient conductor of heat every bit well every bit electricity.
That ways heat and electricity can hands pass through the metals.
#7 High melting point and humid point

The metals take a high melting indicate besides as boiling point.
#8 Hardness
Hardness is the ability of a material to resist wearable, tear, scratching and to resist the changes in shape.
Generally, all the metals testify these properties (except mercury)
(Note: Sodium, potassium and lithium are soft metals which can exist cut with a kitchen knife.)
#9 Density

Metals have high density. And because of this, metals have more weight.
Chemic properties of metal
#1 Valency
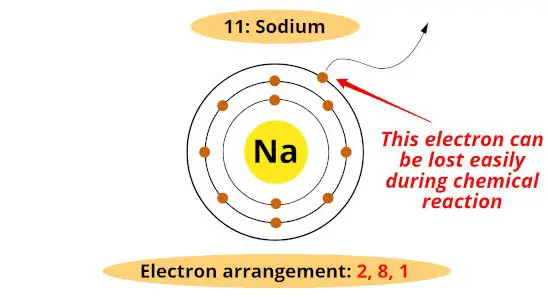
The atoms or metals have generally ane, 2 or iii electrons in the outermost orbit, and they lose these electrons during a chemical reaction.
#ii Corrosiveness

Some metals get corroded easily when they are exposed to moist air or water (For case: Iron)
#3 Loss of electrons

Metals have a trend to lose electrons. They donate electrons during a chemical reaction.
#4 Low electronegative
Metals are less electronegative then they are electropositive in nature.
#v Reactive
Some metals are chemically more reactive. They undergo chemical reactions by themselves or other elements and release energy.
For instance: Potassium gets ignited automatically when it is exposed to water.
#6 Forms bones oxides
Metals react with oxygen and grade basic oxides.
#7 Good reducing agents
Metals are reducing agents because they donate electron/due south during a chemical reaction and get oxidized.
Gratis Gift for you: Interactive Periodic Table
Permit me tell you how this Interactive Periodic Tabular array will help y'all in your studies.
1). You can effortlessly find every single detail almost the elements from this single Interactive Periodic tabular array.
ii). Yous volition get the detailed information near the periodic table which will convert a newbie into pro.
3). You will also go the Hd images of the Periodic tabular array (for FREE).
Checkout Interactive Periodic tabular array and download it's loftier resolution epitome now (It'southward FREE)
Summary
So in the entire article, we have discussed the location of Metals on the Periodic table.
Nosotros saw the;
- Position of Brine Metals,
- Position of Alkali metal Earth Metals,
- Position of transition metals,
- Position of Inner transition metals,
- Position of Rare earth metals,
- Position of Heavy metals too as reactive metals.
Then we discussed the consummate list of all the metals of the Periodic table.
I gave you lot the reason why the metals are located on the left side of the Periodic table.
And finally we discussed the physical and chemic properties of metals.
I promise this article "Where are Metals located on the Periodic Table" has helped you in solving your queries.
Suggested Of import articles for yous:
- Everything you demand to know about the periodic tabular array
- Periodic table with different types of metals
- Nonmetals on the periodic table
- Metalloids on the periodic table
- Periodic table labeled with metals nonmetals and metalloids
- Halogens on Periodic table
- Noble gases on periodic table
- List of elements of Periodic table
- Periodic tabular array with electron configuration
- How are the elements arranged in the mod periodic tabular array?
Periodic Table Of Heavy Metals,
Source: https://periodictableguide.com/metals-located-on-the-periodic-table/
Posted by: dooleycitage.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Periodic Table Of Heavy Metals"
Post a Comment